Services
SERVICES
SOLUTIONS
TECHNOLOGIES
Industries
Insights
TRENDING TOPICS
INDUSTRY-RELATED TOPICS
OUR EXPERTS

September 25, 2025
Identifying and addressing potential security vulnerabilities in an organization's IT infrastructure is the first step in minimizing the risk of successful cyberattacks. AI technologies can be used to enhance key vulnerability management tools and techniques, including:
While traditional cybersecurity tools follow predefined rules to detect potential threats, such as a number of failed login attempts exceeding a threshold, AI systems use machine learning algorithms to autonomously identify patterns and anomalies associated with an attack. This flexible approach, which helps address complex or new scenarios not covered by rigid rules, can be applied to different types of security threats:
With their combination of advanced decision-making and automation capabilities, AI-powered cybersecurity tools can analyze security incidents and choose the best course of action to address them with minimal human intervention. This process typically includes:
In an ever-evolving field like cybersecurity, gathering information on existing or emerging types of threats, attack vectors, and malicious actors and keeping up with new cybercrime trends enables organizations to set up protection mechanisms for a more robust security posture. Cyber threat intelligence embraces this proactive approach and AI tools powered by natural language processing and GenAI can help in this regard by:
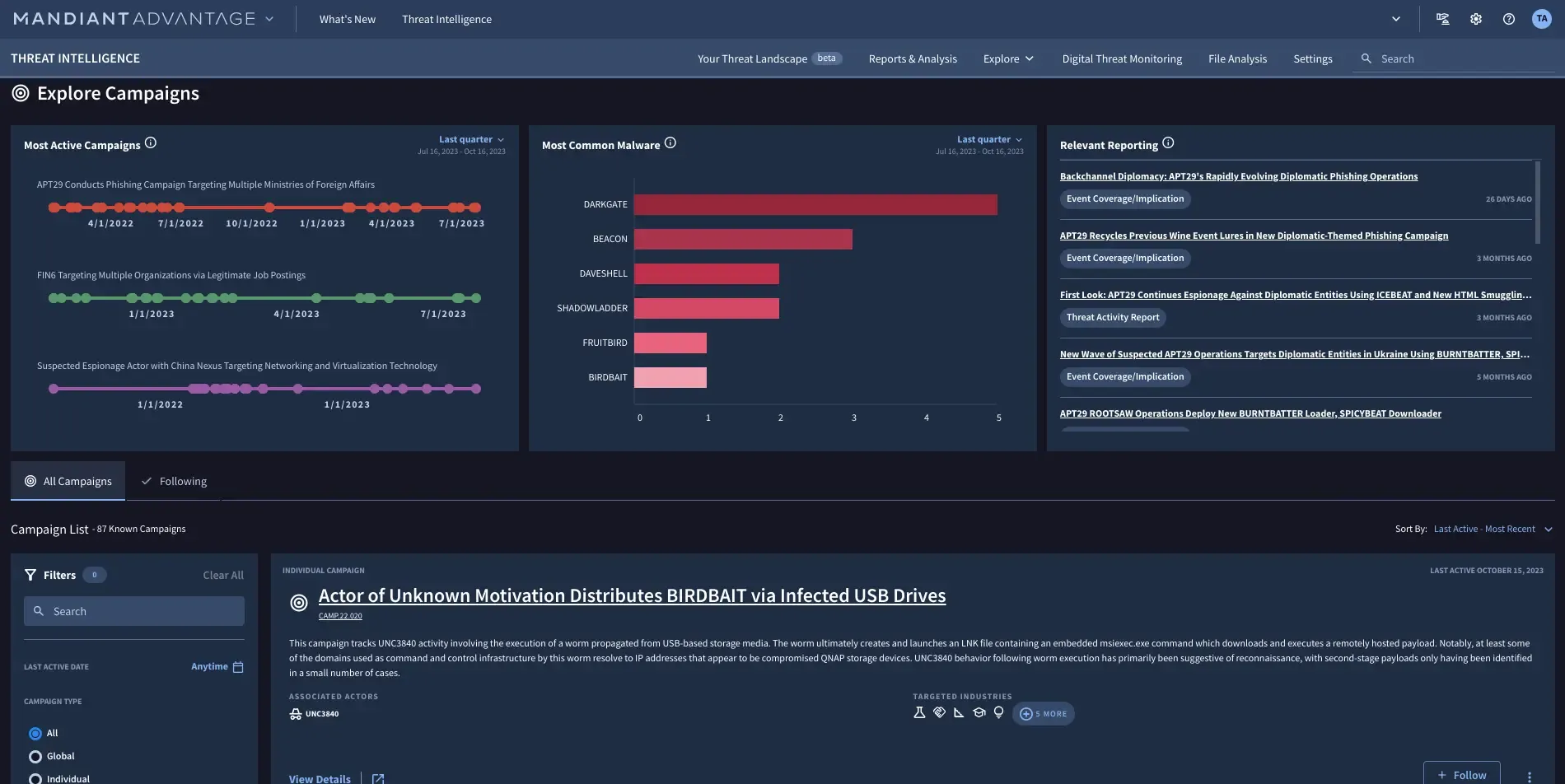
Image title: Google Threat Intelligence’s report on active threat campaigns Image source: Google Cloud
| The AI in cybersecurity market was valued at $24.3 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $134 billion by 2030 | |
|---|---|
| 43% of organizations currently use artificial intelligence as part of their cybersecurity strategies | |
| 64% of cybersecurity professionals surveyed are researching GenAI-powered security tools or have already purchased one. 76% of respondents are opting for GenAI tools specifically designed for cybersecurity rather than domain-agnostic solutions | |
| 80% of security specialists prefer GenAI delivered through a comprehensive platform rather than more specialized point solutions. Specifically, these experts believe that platform-based options lead to faster returns, reduced security incidents, fewer training cycles, and lower maintenance costs |
Scheme title: Most popular use cases of AI in cybersecurity
Data source: Statista
Scheme title: Cybersecurity areas where defensive AI is expected to impact the most
Data source: Darktrace
| The top cybersecurity use cases where organizations plan to use GenAI include rule creation (mentioned by 21% of respondents), cyberattack simulation (19%), compliance violation monitoring, and network detection (16%) |
|---|
| 95% of security teams surveyed believe AI can improve the speed and efficiency of cyber defense, and 88% of teams are already seeing significant time savings from AI adoption | |
|---|---|
| 71% of organizations report higher job satisfaction among their cybersecurity specialists due to AI automating tedious security tasks | |
| 58% of cybersecurity professionals think that artificial intelligence will enhance or support them, while only 12% expect it to completely replace their role | |
| 63% of cybersecurity specialists expect AI to help strengthen security measures, especially in terms of threat detection and response capabilities | |
| According to cybersecurity leaders, the security market segments that will benefit the most from GenAI include cloud security (mentioned by 55% of respondents), security operations and management (52%), and endpoint security (52%) |
Top concerns about AI adoption in cybersecurity among specialists
Data source: CSA
| 51% of stakeholders in very large organizations (25,000+ employees) expressed a lack of confidence in AI-powered cybersecurity solutions | |
|---|---|
| 18% of security leaders believe that AI devices currently offer less value than any other security solution when taking into account initial investment, time, and operational costs | |
| 56% of organizations surveyed reported that their AI solutions were unable to effectively identify new threats due to poor training data quality |
AI-based security systems prove more effective than traditional solutions thanks to their specific approach to threat detection and response.
Unlike traditional tools that use rigid, manually compiled rules based on past security events, AI-enabled systems continuously learn patterns and anomalies from new event data, incorporating this knowledge into their models to adapt to evolving threats.
The adoption of AI enables a more proactive approach to cybersecurity, as adopters can gather information on the most common threat scenarios to increase their readiness or identify vulnerabilities in IT systems to reduce their cyber exposure with preventative measures.
AI’s ability to identify nuanced patterns and relationships across a wide range of variables enables AI systems to achieve lower false positive and negative rates than rule-based security tools that rely on a less flexible "if/then" logic.
Since AI-powered cybersecurity solutions don’t need precompiled rules to operate and typically generate less false positives than traditional systems, cybersecurity teams won’t be overwhelmed by time-consuming rule updates or manual reviews to verify false alarms.
While the use of AI in the cybersecurity sector is on the rise, many companies struggle to fully seize the benefits of this technology. Here are some key aspects to consider.
The AI model powering a security system requires vast amounts of data to learn the patterns or anomalies recorded during security events and recognize them once they recur in future attacks. Therefore, you need to make sure these large training datasets contain relevant and accurate data. For example, training your AI system on properly labeled data points from thousands of failed login attempts will help the solution recognize unauthorized login attempts. That said, this process can be very demanding in terms of training time, IT infrastructure, expertise, and upfront investment.
In most cases, adopting AI algorithms requires adjustments to a company’s workflows and cybersecurity practices. To facilitate this transition, create a dedicated governance framework establishing the roles of cybersecurity professionals, continuous AI model output supervision and fine-tuning via retraining iterations, routine risk assessment, and a backup plan in case of AI system failure.
Itransition’s team provides AI services and solutions to help organizations strengthen their cybersecurity capabilities and minimize business risk.

Our team builds ML solutions that balance high performance with usability, handling everything from data preparation and model training to front- and back-end development, system integration, and post-launch support.
We provide expert support at every stage of the ML implementation journey, from business needs assessment and solution design to project planning, oversight, and user onboarding, ensuring the final system aligns fully with your expectations.
The adoption of artificial intelligence is not the savior of legitimate organizations, but a full-blown arms race between companies and cybercriminals. While hackers are actively looking to exploit the latest technological advancements for malicious purposes (think password-guessing AI), businesses should be ready to use those same tools to improve their own cyber readiness.
If you're looking for a robust AI solution to withstand even the most sophisticated cyber threats, consider building one tailored to your needs with Itransition's expert guidance.

Insights
Find out how ML for fraud detection works, along with key use cases, real-life examples, and the benefits and challenges of adopting this advanced technology.
Service
We provide businesses with a broad range of cyber security services, covering all types of organizational IT assets. Get our assistance

Insights
Explore 11 use cases, types, pay-offs, and best practices of machine learning for anomaly detection.

Case study
Here’s how Itransition developed an educational portal with content and learning management capabilities and robust security features for an insurance company.

Insights
How to achieve unfailing IIoT security? Explore the most common threats and develop a feasible strategy to effectively overcome them.

Insights
Learn about the most pressing security issues and threats for online ecommerce businesses and discover the most effective measures to avert them.
Services
Industries