In one of his biggest hits, the American singer Meat Loaf reminds us that "Objects in the rear view mirror may appear closer than they are", turning the familiar safety warning into a metaphor for the excessive importance we often give to past events and circumstances.
As you might expect, the old memories still haunting the song's protagonist had little to do with business. However, decision-makers can learn something from this refrain. Indeed, while no one would ever deny the importance of gathering and analyzing historical data to frame current scenarios, it's also true that a snapshot of the past is simply not enough to understand the present, especially in a world changing faster than ever.
What is “breaking news” right now may be too old and not relevant enough from a business perspective in a couple of days, and this is the challenge that operational business intelligence aims to overcome.
What is operational business intelligence?
Operational business intelligence, also referred to as OBI or just operational intelligence, is an ensemble of technologies and techniques BI consultants implement to constantly monitor current business data, assess corporate processes in real-time, and identify potential opportunities.
This approach typically relies on data gathering, warehousing, analysis, and visualization tools designed to better peer into an ongoing stream of fresh information instead of just focusing on historical data. Such features make enterprise OBI particularly effective in providing valuable insights on a regular basis and enabling them to take immediate action, especially when dealing with ever-evolving business scenarios and dynamic market or customer trends.
They also promote data democratization by keeping track of several KPIs and visualizing them through intuitive dashboards to facilitate their interpretation and further speed up data-driven decision-making.
Traditional vs operational business intelligence
OBI certainly shares a variety of tools and methods with standard BI, as the analysis of business data to set up effective corporate strategies, enhance performance, and increase revenues represents the ultimate goal of both disciplines. The path followed by OBI to achieve it, however, differs in many respects from its more traditional counterpart.
So, what’s the difference between BI and OBI? Let's highlight their peculiarities to help you select the best option when investing in business intelligence services.
1. Focus
While traditional BI primarily aims at investigating data to frame major business trends and growth drivers, OBI prioritizes the analysis of specific events or corporate processes to identify inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement. Therefore, we may say that BI follows a comprehensive, data-centric approach, whereas OBI can be considered as its activity-centric sub-branch.
2. Scope
As a consequence of the first point, the extent of BI's analyses is generally broader than OBI since they are based on huge datasets encompassing a vast range of variables, such as marketing campaign parameters, sales data, supply chain metrics, customer churn rate, and many more. This means that BI can be a valuable tool for improving long-term, strategic decision-making.
OBI, on the other hand, can typically shed light on particular operations and business functions from a tactical perspective, somehow replicating in the realm of data analysis the dualism existing between BPM and RPA in the process management domain.
3. Timeframe
Traditional BI follows the good old rule of "exploring the past to understand the present and predict the future" as it involves the collection and storage of historical data that will later be used to clarify the underlying dynamics driving certain trends or phenomena.
This long and demanding procedure ensures accurate analyses and forecasts, as it allows us to identify business-related patterns that may recur in the future under the same conditions. However, it takes time and implies the risk of turning historical data into obsolete information, especially when the state of the market and the business scenario in which we operate change dramatically.
Operational business intelligence, instead, is all about the present. The idea is to ensure non-stop, real-time visibility into business operations, as its name actually suggests, and provide managers with timely feedback that will help them fine-tune the corporate workflow on a daily basis.
4. Approach to data
The approach adopted by BI to leverage data and get business insights can be described as reactive. In fact, it implies the "on-demand" analysis of data which had been previously collected from selected sources (typically corporate systems such as CRM, ERP, or HRMS, along with external databases), transformed according to business logic, stored in a data warehouse or data lake and kept ready for future use.
OBI, on the other hand, opts for a proactive approach, as a constant stream of operational data flows directly from the aforementioned data sources to an analytical platform without being warehoused. This allows managers to oversee day-to-day processes and actively track business performance.
5. Business scenario
When it comes to investigating the grand scheme of things, such as the mysterious cause-effect relationships between apparently unrelated macro-trends, the best discipline to count on is probably business intelligence, given its focus on the detection of recurring patterns and anomalies.
This can be the case if we're dealing with a challenging business scenario involving a long-term decrease in sales performance despite successful marketing campaigns and the lack of competitors, which may be due to poor logistics and, consequently, excessive delivery times, poor customer satisfaction, and high churn rate. BI helps to identify such issues and, therefore, select a proper solution.
But when the scenario being faced requires accurate supervision of specific business operations, solid situational awareness, and superior responsiveness to ever-changing market conditions, OBI is the best bet. Using the example above, companies might notice an increase in delivery times due to a peak in demand (remember the times of quarantines and curfews?) or extensive road maintenance interventions. In this situation, OBI solutions can help speed up shipping procedures by calculating the best delivery routes based on driver feedback, combined with real-time weather and traffic data.
6. Technologies
The different roles and methods of BI and OBI impact the selection of instruments they rely on to fulfill their purpose. Business intelligence draws heavily on the tech array of data science and data analytics, implementing a comprehensive set of software solutions and features to harvest and sift through large datasets.
These encompass, for example, on-premises and cloud data integration solutions and ETL systems to extract, transform, and load data, along with data stores such as data marts and data warehouses, algorithm-based data modeling software to uncover relationships or patterns, and data visualization solutions to easily grasp and share business insights.
OBI taps into these technologies too (see our article on data warehouse modernization) but complements them with specific tools and techniques that speed up data cleansing and processing and allow businesses to better handle an ongoing stream of data for real-time analysis. However, this topic deserves its own section.
| BI | OBI | |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Major trends | Specific activities |
| Scope | Strategic | Tactical |
| Timeframe | Long-term | Real-time |
| Approach to data | Store and then analyze | Analyze and then store |
| Business scenario | Framing broader dynamics and patterns | Optimizing operations “on the ground” |
| Core technologies |
ETL Data warehouses Data modeling |
Real-time monitoring Complex event processing Dynamic dashboards |
Get OBI solutions from Itransition to fuel your business with data
Operational business intelligence tech stack
As in any other discipline, the OBI toolkit basically reflects its raison d'être, namely opening a window into current business scenarios or corporate operations and providing your staff with prompt, actionable insights in the most intuitive way possible. Here are some software solutions, features, and techniques that are commonly adopted in this regard:
Complex event processing
Complex event processing engines or simply CEP act as the analytical core of OBI, as they're capable of processing rapid streams of data with powerful algorithms to identify patterns and real-time events, i.e. changes of state occurring when certain parameters exceed a predetermined value.
These events may imply particularly favorable market conditions and business opportunities to seize faster than competitors, such as profitable stock price fluctuations. However, they might also represent suspicious anomalies heralding potential risks, like a spike in login attempts interpreted as a sign of upcoming cyberattacks or fraud. Be it good or bad news, the meaningful and timely insights extracted from data streams via CEP allow enterprises to react quickly and accordingly.
Business activity monitoring
Like an (almost) omniscient overseer keeping an eye on a multitude of events, business activity monitoring software or BAM supervises the business activities fueling an enterprise and provides managers with regular feedback on the corporate workflow. Its main tasks include:
- Aggregation and analysis of real-time operational data of different formats and coming from a variety of sources to spot tendencies, emerging opportunities, inefficiencies, and potential areas of improvement.
- Report automation to offer day-to-day visual insights and recommendations, ensuring end-to-end visibility into key business functions (marketing and sales, finance, stock management, etc.), and enabling managers to make informed decisions easier and faster.
- Alerts and notifications triggered under certain conditions to minimize operational risk and improve management's reactivity to unexpected events, such as stockouts, bank account balance and sort code variations, or unauthorized transactions.
Business process management
OBI and business process management (BPM) share the common goal of analyzing and enhancing business processes and operations, which makes them ideal partners. Indeed, BPM suites are commonly deployed in the realm of operational intelligence to fine-tune and harmonize the business workflow across the organization, allowing companies to improve performance without having to resort to additional resources.
This optimization procedure is typically performed by identifying business weaknesses or bottlenecks through data analysis and by redesigning or automating via AI and RPA all those corporate functions that have proved not sufficiently efficient and synergistic. A critical step in business process design involves the creation of graphical representations known as BPMN models, which portray the reorganized business processes and policies and can be simulated via BPM software to assess their potential outcomes.
Real-time dashboards
When overwhelmed by a non-stop stream of live information, any decision-maker would choose to consult clear and insightful dashboards rather than endless spreadsheets. That's why OBI solutions (including the aforementioned BAM systems) are generally equipped with efficient, user-friendly data visualization tools designed to facilitate the querying and interpretation of business data, even among non-tech-savvy professionals.
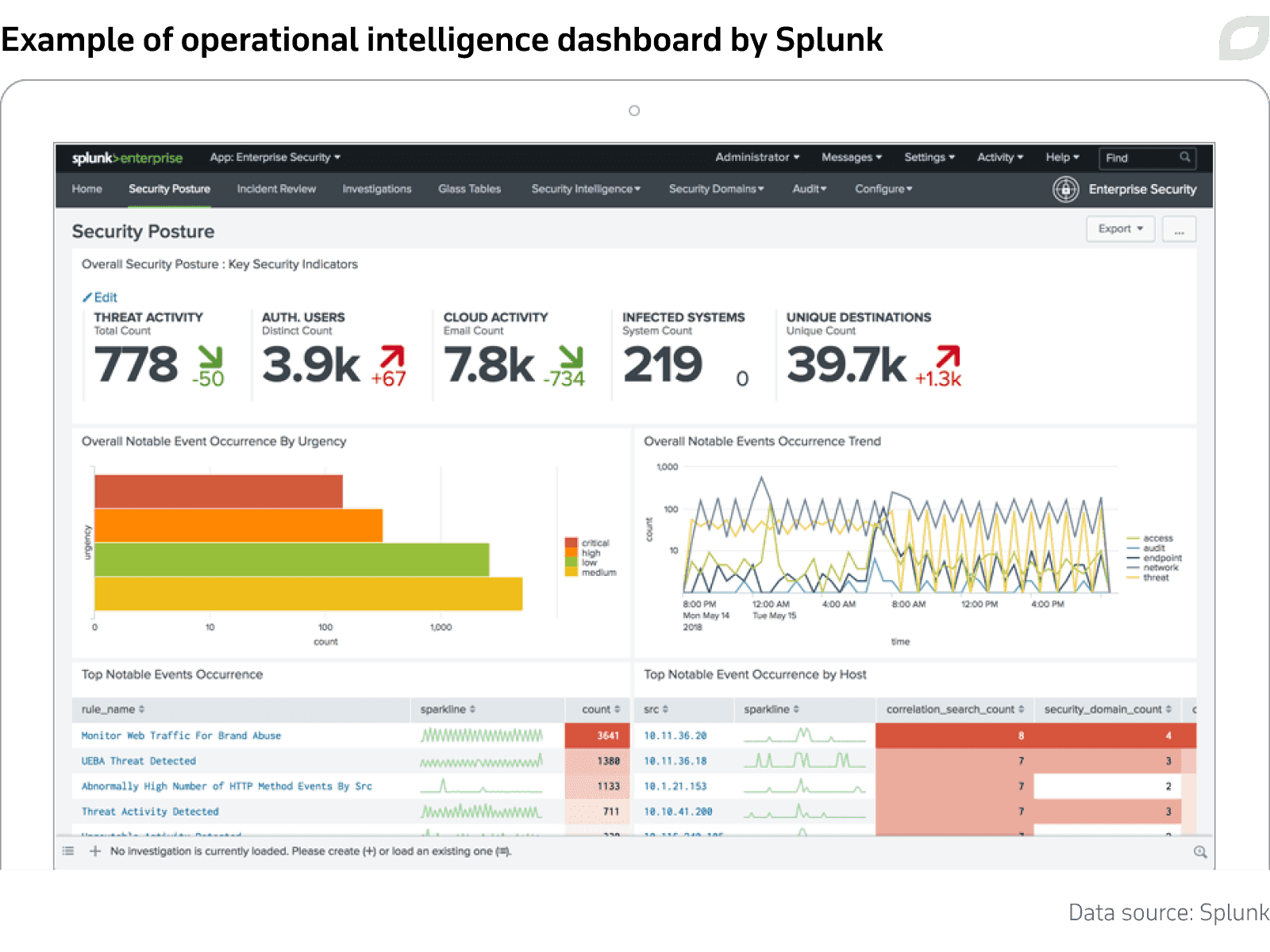
Of course, data visualization represents a growing trend in several data analytics-related fields, including traditional BI. However, OBI-focused dashboards come with their own specific features to adapt to the operational and somewhat ephemeral nature of data that this discipline has to manage.
These may include a tighter refresh rate to keep up with constantly evolving KPIs, along with highly customized interfaces with different templates or storyboards based on user role, since OBI is meant to be an actionable tool "for everyone". And this brings us to the top benefits of operational intelligence.
OBI payoffs and opportunities
If we were to summarize the most important merits of OBI, we might mention its ability to fully embrace and embody the core principles of augmented analytics and augmented business intelligence in real-life scenarios. These cornerstones involve the adoption of advanced technologies, such as AI and machine learning, to automate and speed up the generation of insights from data while making them available to a wider pool of professionals.
This translates into two core benefits provided by OBI:
1. Enhanced decision-making
At this point, it should be clear that OBI solutions are built on top of a tech stack that ensures seamless monitoring and real-time analysis of any business-relevant parameter. This enables them to provide enterprises with immediate operational insights, recommendations, and triggered alerts.
The major result of this ongoing supervision is the acceleration of decision-making procedures and greater corporate adaptability to changing business conditions. In this regard, it's worth reporting the results of BARC's Top Business Intelligence Trends 2022 survey, which highlighted the importance of real-time data analysis for BI professionals.
2. Data democratization
Businesses are certainly not armies. However, they are both structured as sprawling, hierarchical organizations and share an essential aspect in terms of decision-making: while most of the key strategic directives are established by corporate executives (i.e. generals), their actual implementation on the ground, along with any tactical choice during everyday operations, typically represent a prerogative of team leaders (i.e. sergeants). This also implies that making relevant information available only to top managers and professional analysts can severely hamper the operational capabilities of a company.
With this in mind, it's not surprising that OBI platforms are generally designed to follow the core guidelines of data democratization, a growing trend encompassing data analytics and business intelligence and aimed at expanding the audience of such disciplines. Among the features that can help make corporate data more accessible and easier to interpret, even for front-line employees with limited analytical expertise, we can certainly count the aforementioned dashboards, along with visual reports, charts, and other data visualization solutions.
OBI software can also be equipped with natural language processing-based features to streamline data querying via conversational interactions. By relying on such instruments, junior and middle-level managers can keep an eye on day-to-day activities and take action responsively, without necessarily having to wait for instructions from the executives.
Shape your BI platform with Itransition’s guidance

Business intelligence
We help enterprises design and implement impactful BI ecosystems to get the most out of their corporate data assets and upscale their decision-making.
Operational business intelligence use cases
We've previously detailed the archetypal business scenario where OBI can be successfully deployed, but let's complement this with some practical examples of industries and corporate functions which may benefit from the adoption of OBI software:
- Logistics: OBI offers a constant overview of the supply chain, including inventory levels, expiration dates, and delivery times.
- Manufacturing: OBI represents an essential tool to monitor production lines and machinery and therefore improve asset performance management and maintenance.
- Retail: Thanks to OBI, retailers can keep track of expiration dates, product demand variations, and in-store staff allocation.
- HR: Human resources managers rely on OBI to analyze staff performance, optimize their workload, and monitor recruitment conversion rates.
- Marketing and sales: OBI can be leveraged to analyze the results of social media campaigns and adjust targeting criteria accordingly.
- Finance: OBI platforms provide financial organizations with timely insights and alerts on stock and currency exchange rate fluctuations or potential fraud attempts.
- IT: OBI software is commonly used to supervise corporate IT infrastructures or networks and quickly react to any malfunction or cyberattack.
Overcoming the adoption challenges
Like every major aspect of digitalization, the implementation of operational BI is not always as straightforward as you might hope. Here are a couple of potential obstacles you should be prepared to overcome before and during its deployment:
- Quality/speed trade-off: One of the most challenging steps of OBI software design is achieving the delicate balance between data quality and data processing speed. Indeed, particularly strict data cleansing requirements may lead to excessively long data preparation procedures and delayed business insights, which is exactly the nemesis of OBI. Therefore, developers and enterprises should find a reasonable compromise between these two payoffs, based on the company's goals, needs, and operational scenario.
- Staff’s concerns: As we described in our recent article on knowledge management strategies, providing particularly "democratic" tools to get and share information doesn't necessarily imply that everyone within a certain organization will be ready and willing to use them. It may be a problem of outdated corporate culture, a general lack of tech skills, or the intricacies of reorganizing roles and processes to implement these new analysis tools in the corporate workflow. Promoting innovation and digital literacy with targeted training initiatives may be a good start to fixing these issues.
Why not both?
BI and OBI opt for divergent approaches to data management and analysis and can count on different tricks up their sleeves. However, these two disciplines are not mutually exclusive and can perform at their best when combined.
Traditional business intelligence helps us understand the past to identify the origin of current trends, while operational business intelligence improves our ability to seize the precious opportunities that the present offers us. As Eleanor Roosevelt, Bil Keane, and Master Oogway, the elderly tortoise mentor of Kung Fu Panda said, “Yesterday is history, tomorrow is a mystery, but today is a gift. That’s why it is called the present".



