Services
SERVICES
SOLUTIONS
TECHNOLOGIES
Industries
Insights
TRENDING TOPICS
INDUSTRY-RELATED TOPICS
OUR EXPERTS

October 9, 2025
Scheme title: US virtual reality in retail: revenue growth forecast (2018–2030)
Data source: Grand View Research
the projected virtual reality market size by 2029
of brands using AR say it helps to drive sales, acquire new customers, and drive performance metrics
of consumers are interested in using AR to interact with a product before buying
Depending on specific business objectives, virtual retail solutions differ in their level of immersion and interactivity, as well as in the range of features they offer, accessibility across devices, and integrations with a broader retail ecosystem.

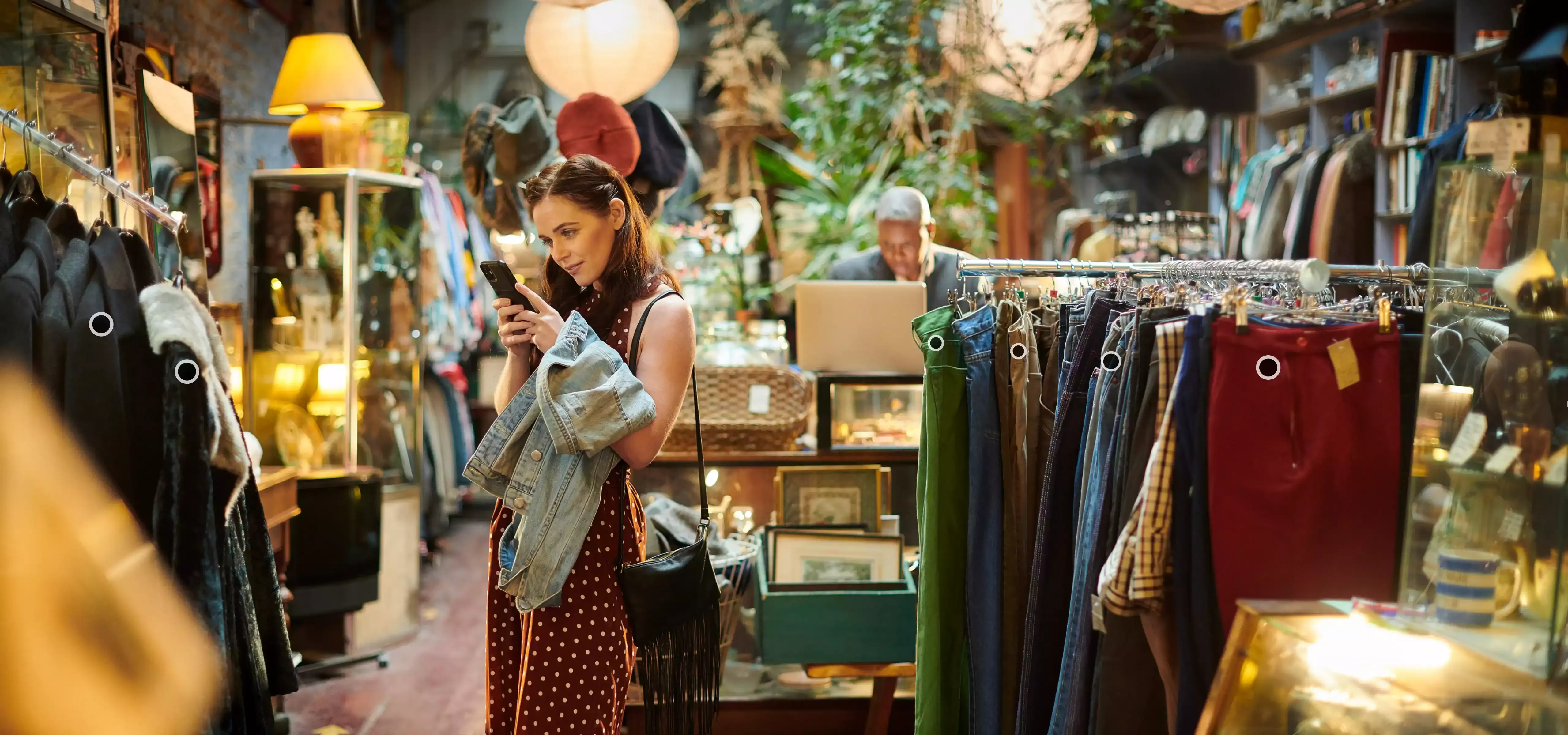
Using a 360-degree viewer in a browser, mobile phone, or VR headset, customers can enter a virtual replica of a physical store, navigate around it, click on products to view details such as descriptions, pricing, and specifications, and complete purchases via an integrated ecommerce checkout.
Customers explore products, navigating an interactive, gamified 3D environment using keyboard, mouse, or touch controls. Shoppers can zoom in, rotate, and interact with detailed product models, which makes the process user-friendly and playful.
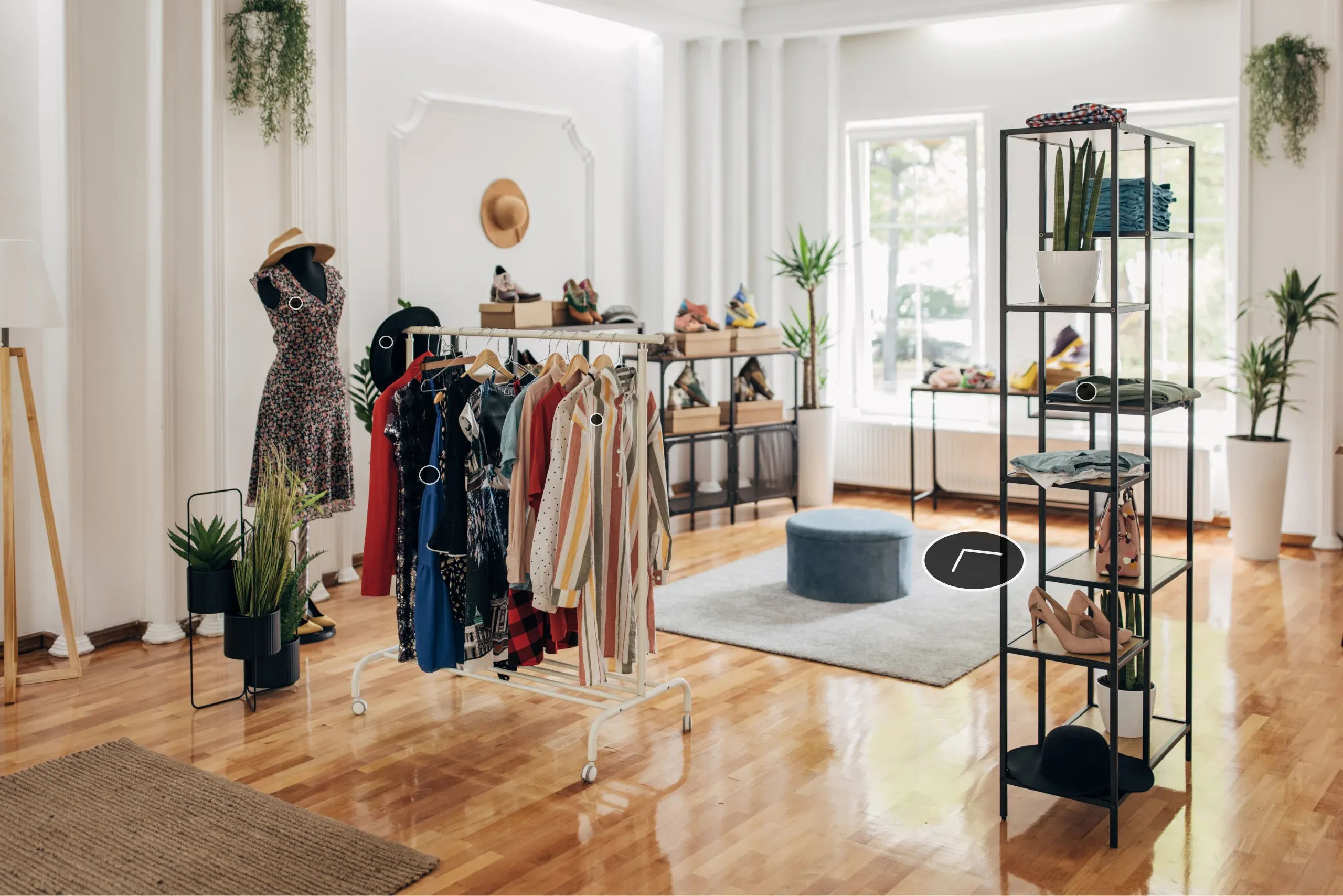
By enabling customers to try on products online, this technology enhances consumers’ confidence in their purchasing decisions and minimizes the likelihood of product returns. Using AR overlays or digital avatars, consumers can assess how items such as clothes, footwear, eyewear, or cosmetics suit and align with their personal style.
With the virtual try-out capability, consumers can visualize virtual items such as furniture, artwork, or kitchen appliances within their real-world environments. Using a smartphone or AR glasses, they can adjust the product’s colors, sizes, and placement to ensure it fits their surroundings and needs.
Live video consultants in virtual storefronts help combine the convenience of online shopping with the value of in-person service. Sales associates guide customers through product choices, answer their questions, and provide personalized advice, bringing a human touch to online experiences.
Augmented reality user manuals enable customers to overlay interactive instructions, such as text or images, directly onto real-word products via a smartphone or AR glasses. This capability helps customers avoid frustration during initial product setup and supports self-service troubleshooting, enhancing the overall post-purchase experience.
For businesses, implementing virtual store environments brings a range of operational and strategic advantages, ranging from optimized internal operations to enhanced responsiveness to shifting customer demands.
Virtual stores enable customers to see how products would look on them or within their personal environment, supporting customer decision-making and consequently increasing sales.
Interactive, immersive environments encourage customers to actively explore products, which helps retailers create emotional connection with their products and increase time spent with their brand.
Virtual stores help companies gather behavioral data, test product placement, evaluate store layouts, and experiment with merchandising concepts that would be too costly and complex in physical stores.
Since customers can explore and try on products virtually, they feel more confident in their purchase decisions, which reduces the risk of mismatches in customer expectations and product returns.
Virtual stores and the immersive user experiences they create help retailers stand out in the market and increase brand visibility through organic customer sharing and social media coverage.
Retailers can train new hires in the safe environment of virtual stores, where employees can learn common store operations and customer interaction protocols. This minimizes the risk of business process disruptions and streamlines employee onboarding.
Virtual stores remove geographical and physical boundaries, enabling customers to interact and shop for products without location or time restrictions.
Since there is no limit to the number of products displayed, virtual stores enable retailers to offer a wider selection of products, which ultimately enhances customer satisfaction.
Virtual retail experiences rely on digital technologies that recreate physical store elements in an interactive online setting, providing the foundation for engaging, realistic, and interactive shopping experiences.
Augmented reality enhances the physical shopping experience by overlaying digital content, such as product 3D models, usage guide, or contextual instructions, onto the real world through a smartphone or smart glasses to enable product try-ons, in-home item placements, and reduce purchasing uncertainty.
Virtual reality allows retailers to create computer-simulated shopping environments that either replicate physical stores or introduce entirely new ones. Using VR headsets, customers can walk through the shopping isles, engage with products in a life-like manner, and interact with virtual shopping assistants.
Computer vision allows the virtual store solution to recognize and respond to customer gestures and facial expressions, enabling natural interactions and more intuitive user experiences.

Being foundational to creating personalized and immersive shopping experiences, AI and ML technologies power recommendation engines that deliver tailored product offerings based on browsing behavior and facilitate 24/7 customer support with AI chatbots and virtual shopping assistants.
Integration with retail IoT enables the seamless ingestion of real-time data, including inventory levels, customer movement, environmental conditions, into virtual store environments to ensure the digital experience aligns with the physical world.
AiBUY offers a platform that transforms live and recorded video sessions into immersive shopping experiences, helping brands drive customer engagement and conversions. Powered by machine learning algorithms, the solution analyzes over 1.5 million images to recognize products within videos or recommend the closest matches. This way, the platform allows customers to watch videos showcasing products and purchase items directly from the stream, providing a seamless and uninterrupted shopping experience.
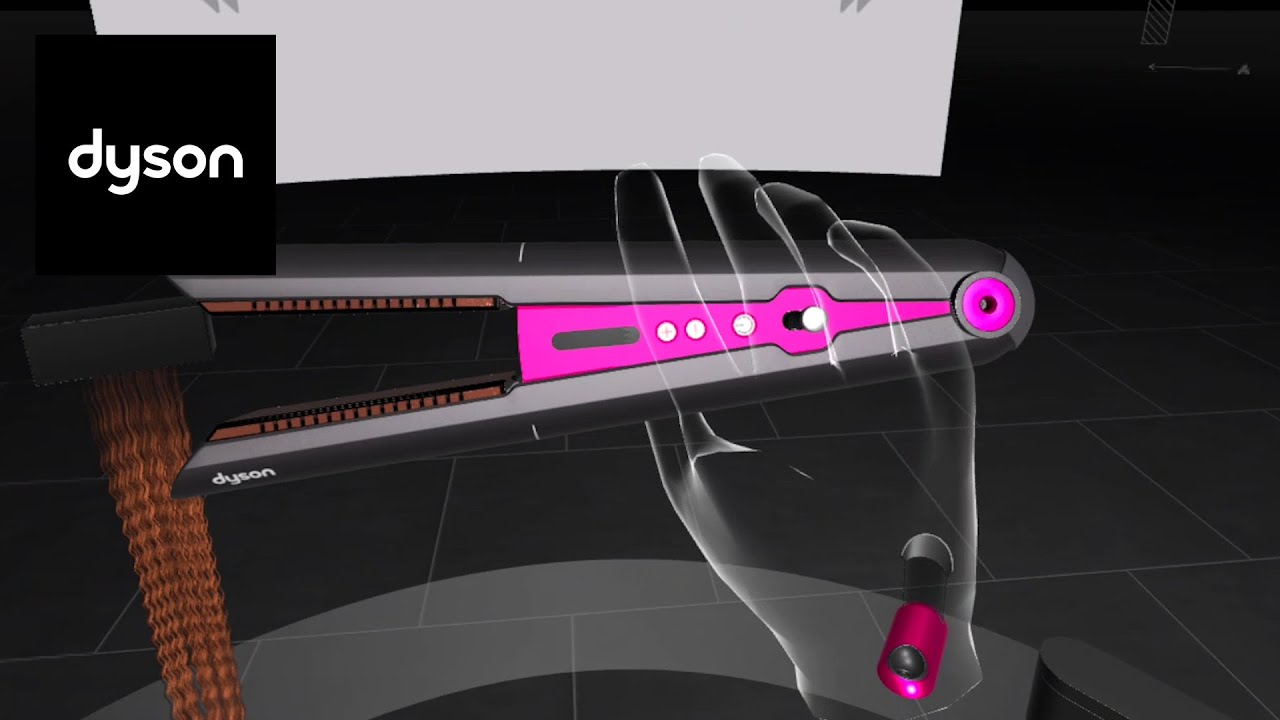
Dyson, a British technology company, allows its customers to interact with products through its virtual reality store. Customers can clean the floor with Dyson’s latest cordless vacuum or experiment with different hairstyles using its hairdryer. To ensure actual representation, Dyson employs high-precision 3D modelling technologies, mirroring those used in its R&D processes, to create virtual environments that reflect the true dimensions and performance of its products.
Sephora, a global beauty brand, has released an AR app that allows users to virtually try on makeup products before purchase. The AI-powered solution accurately detects facial features, such as eyes, lips, and cheeks, for product application and lets shoppers see how skin foundations, eyeliners, and lipsticks will look on their faces. The app also provides personalized product recommendations and step-by-step virtual makeup tutorials. Within eight weeks of the launch, the app recorded 1.6 million visits and 45 million try-ons, highlighting strong user engagement.

Ralph Lauren, a global fashion brand, created a virtual version of its Beverly Hills flagship store called The 888 House using WebAR technology. Customers can navigate the store directly via a web browser, no app or headset required, explore clothing and accessories displayed on mannequins and tables, and view product details with direct links to purchase online. Background music and lighting replicate the atmosphere of the brick-and-mortar store to create a fully immersive experience for shoppers.

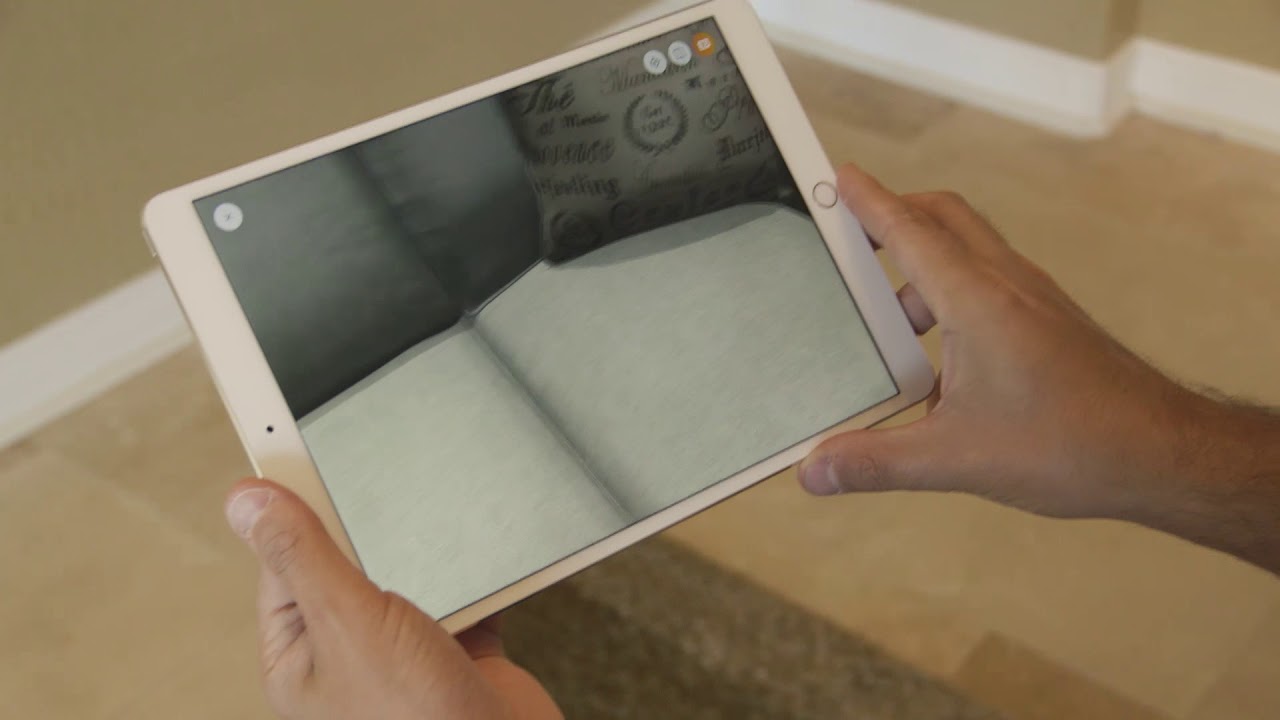
Ashley Furniture has launched two immersive 3D shopping solutions, a virtual showroom and a mobile app, designed to improve the way customers explore and select furniture. The Ashley 360 in-store VR showroom allows shoppers to plan and customize room layouts using an iPad-based design tool, then view them in a full 360-degree environment through HTC Vive headsets. Complementing the in-store experience, the Ashley HomeStore iPhone app allows users to preview the same furniture pieces at home, placing true-to-scale 3D virtual store items directly into their living spaces.

Challenge | Solution | |
|---|---|---|
High technology costs & executive buy-in |
Building and operating virtual stores requires significant investments in technology infrastructure,
development talent, and integration effort. These costs can quickly escalate as the solution evolves and
scales, making it challenging to justify further funding.
| To reduce upfront capital expenditure and demonstrate early value, it is recommended to start the virtual store initiative with an MVP targeting a specific customer segment and a limited, but relevant product assortment. Such an approach allows to validate customer engagement and conversion potential without investing in full-scale online store infrastructure to secure stakeholder commitment for further development. |
Data privacy |
Virtual stores collect vast amounts of personal data, including payment and transaction details, biometric
data, and customer purchase history. Unauthorized access to this data can lead to identity theft, financial
fraud, and reputational damage.
| To minimize the risk of data breaches and misuse, a company must devise a robust data governance strategy, which covers the following aspects:
|
Customer onboarding |
Some customers may perceive virtual stores as another passing trend, rather than an efficient shopping
channel. Combined with usability concerns, such as the necessity to use unfamiliar VR headsets or 3D
navigation, this skepticism can lead to trust issues and low adoption rates.
| To reduce friction and accelerate software adoption, companies should design a deliberate customer onboarding strategy that encompasses:
|
Technology ROI estimation |
Because of the lack of a structured approach for measuring customer engagement in immersive environments,
companies often struggle to evaluate the effectiveness and ROI of their virtual store initiatives. Without
defining clear project success criteria and KPIs, businesses risk implementing innovative technology
solutions that deliver limited measurable impact.
| To secure positive technology ROI, ROI estimation must be built into the early project planning stages. This involves defining key customer engagement parameters, such as time spent in the store, product interactions, or conversion rates from immersive experiences, and aligning them with business KPIs like sales growth, customer retention, or brand awareness. With a well-defined measurement framework in place, organizations can continuously monitor solution adoption and customer engagement, evaluate business impact, and adjust virtual store experiences to maximize long-term returns. |
With solid experience in AR/VR implementation and ecommerce consulting, Itransition supports businesses in integrating virtual store capabilities into their retail systems as well as in designing and implementing comprehensive virtual store ecosystems.
Our experts elicit and analyze your commerce needs and objectives as well as carefully audit your current technology environment to conceptualize a virtual store solution, select an appropriate technology, and develop a step-by-step implementation roadmap, guiding you along the entire project.
We deliver customer-centric virtual store solutions tailored to your specific workflows and customer needs. Our services cover the full implementation cycle, from business needs analysis to post-launch support, ensuring the seamless integration of virtual store capabilities into your daily operations.
The final cost of implementing a virtual store solution depends on multiple factors, including:
The integration of virtual try-on functionality into an existing ecommerce platform typically ranges from $5,000 to $30,000, while developing a full-scale virtual store solution with multiple custom integrations and interactive features, can exceed $100,000.
To learn the ballpark estimate for your virtual store project, reach out to our consultants.
The duration of the implementation project is strongly affected by the app’s functionality and the complexity of its elements and can vary from several months to a year or more.
To extend the capabilities of their virtual stores, companies can integrate them with:
To create immersive and interactive shopping experiences, virtual stores rely on a set of features, including:

Service
Explore our computer vision consulting and development services, along with top branches, use cases, adoption guidelines, tech stack, and benefits.

Service
Explore our range of machine learning consulting services, along with related technologies, use cases, implementation roadmap, and payoffs.

Service
Itransition offers comprehensive ecommerce portal development services to help companies implement high-performance solutions tailored to their business needs.

Case study
Learn how Itransition delivered retail BI and deployed an ML-based customer analytics solution now processing 10TB of data.

Case study
Read the story behind Itransition’s 5-year collaboration with a leading UK furniture manufacturer on web, mobile and VR solutions.