
Enterprise IoT: top 7 use cases, real-life examples, and trends
October 16, 2023

by Max Pliats,
Cloud and IoT Solution Architect
Enterprise IoT application development can provide more visibility and control over enterprise devices and automate operational processes. With sensors and actuators, wearables, devices, and data storing and processing systems, IoT infrastructures help enterprises proactively monitor employees, assets, and facilities, gain insights into the company’s operation, and make smarter data-driven business decisions.
Enterprise IoT market state
With the value IoT technologies can bring to businesses, the enterprise IoT market continues to grow rapidly. Here are some notable figures regarding the fast pace of IoT adoption.
$12.6 tn
the economic value IoT will reach by 2030
- McKinsey
65.2%
the market share that SME segment held in 2021
- Grand View Research
13.9%
CAGR of the enterprise segment from 2022 to 2030
- Grand View Research
Scheme title: Disaggregation of economic value by IoT use-case cluster
Data source: mckinsey.com — The Internet of Things: Catching up to an accelerating opportunity, 2021
The architecture of enterprise IoT infrastructure
An IoT architecture represents a range of interconnected physical devices with sensors and actuators, platforms and applications for IoT management, as well as data storing and processing tools.
Sensors and actuators
Sensors capture the information from the physical environment (e.g., heat, light, pressure, etc.) and by wire or wirelessly transmit it to connected devices. Actuators, in their turn, act on data collected from connected devices and can perform a physical action (e.g., turn on/off ventilation). Both sensors and actuators are configured through the devices they are linked to.
Devices
Devices are hardware components with embedded firmware (routers, smartphones, tablets, etc.) that receive, process, and transmit data from sensors and actuators.
Gateway
IoT gateway, or the abstraction layer, receives data in its primary format from the devices and translates the information into the necessary format, mediating data exchange. It is needed when an IoT device cannot link directly to the IoT platform. In addition, IoT Edge is used when it is more reasonable to collect and process data without actually transmitting it to the cloud.
IoT integration middleware
The IoT integration middleware includes infrastructure and integration layers responsible for the general system functioning, container management, device management, APIs and connectivity management, as well as data storage and analytics mechanisms.
Application layer
The application layer represents the software that requests data from the sensors and performs physical actions through actuators, utilizing the IoT integration middleware. Some business function-specific applications control devices, while others collect and store data that IoT data analytics software processes to generate valuable business insights.
Security
The security infrastructure covers all components of the IoT architecture and ensures data privacy, industry regulatory compliance, and device safety.
Top enterprise IoT use cases

1 Asset tracking
Enterprise IoT can facilitate the management of a distributed ecosystem of high-tech, conventional, stationary, or movable physical assets. Uniting the wealth of equipment, devices, and other assets into a single IoT ecosystem, companies can keep track of their location and get credible information on each item’s state anytime. Apart from ensuring accountability, the system helps protect the assets from theft and detect their location accurately in case of loss.
2 Predictive maintenance
IoT solutions in enterprise buildings can automate the process of office equipment maintenance. By gathering data on equipment exploitation, performance, energy consumption, errors, and updates, IoT sensors help monitor the condition of all types of office equipment, from HVAC and smart locks to laptops and printers. Such continuous monitoring makes it possible to timely alert the team when the appliances require maintenance before the actual breakdown.
3 Employee and office security
The activity information from each IoT-enabled device can be instantly transmitted into a unified database, creating a steady digital trail of all security events within the enterprise. In case of intrusion on-premises, this information can be passed on from surveillance cameras to door locks, immediately blocking the closest ones and thus stalling the perpetrator’s progress. With suitable devices in its infrastructure, enterprise IoT solutions can also enable access control through facial identification, voice and biometric recognition, movement tracking, and intelligent door-locking systems. Every lock in the building can have an access controller and require a card with an assigned IP address to enter the room.
4 Smart light and HVAC control
Smart lighting systems encompass digital and motion sensors, communications interfaces, actuators, and lighting devices. They are programmed to operate remotely and can be used to change the light spectrum and color or adjust the level of illumination when a motion sensor detects activity. IoT sensors allow the HVAC equipment to measure air temperature, humidity, and purity, consider weather predictions, and monitor HVAC usage trends, so the indoor climate always stays optimal for employees.
5 Occupancy monitoring
IoT technologies can also prove valuable for building and workspace occupancy monitoring, allowing for real-time space management and efficient resource allocation. IoT technologies provide real-time data on space, meeting rooms, and desk utilization with cameras, infrared sensors, and access control tools installed across office facilities. As a result, such occupancy monitoring solutions provide accurate insights into how effectively the office space is used and help make data-driven decisions on space allocation, saving costs on unused desks and rooms.
6 Smart energy management
Enterprises can utilize IoT solutions to monitor and control energy consumption in their commercial buildings. Smart sensors collect data on energy usage, HVAC utilization as well as facility occupancy to determine electricity overconsumption and optimize lighting and heating patterns across the building. For instance, the IoT infrastructure can detect that the C-suite uses the meeting room once every two weeks and reduce the temperature there for the period of non-use. This way, IoT will help save money on energy bills and reduce environmental impact.
7 Smart parking
IoT can help large enterprises with numerous car owners optimize their parking. Companies can ensure only their employees have access to the parking spaces by implementing intelligent parking systems where the parking gate arm opens with a smartphone or a special remote controller. They can also apply visual image processing and optical recognition technology to identify the car and automatically open the gate to the parking lot. Enterprises with large parking areas can also utilize the system’s hardware sensors to detect available parking slots and communicate the information to the drivers via their smartphones.
Thinking about adopting IoT for your enterprise?
Examples of IoT for enterprises
Let’s explore real-life cases of how IoT technologies transform traditional enterprise environments.
Smart lighting for Bravida’s office
When moving to a new office, a Swedish installation company Bravida decided to implement a smart lighting technology to ensure proper and even lighting and to meet the indoor lighting norm. For this, Bravida took the initiative to implement AI-powered lighting controls. Lamps communicate with each other wirelessly using built-in nodes and sensors connected to the main LED driver. The lights switch off automatically after 15 minutes of space vacancy to save energy. Since the rooms in the office have transparent walls, the lights outside a room in the corridor are kept turned on when the room is in use for additional comfort of the employees.
Cisco’s intelligent parking system
In its Frankfurt office in Germany, Cisco adopted an IoT technology to solve the shortage of e-parking spaces. Cisco equipped parking with LoRaWAN parking sensors and created a website where users can check the availability of parking spaces in real-time. The system also analyzes parking usage over time and creates dashboards showcasing the number of parking processes per parking space and time/date. Moreover, users can receive push notifications when all parking spaces are occupied or only one is available. Employees can also ask the ParkingBot which parking spaces are empty or occupied.
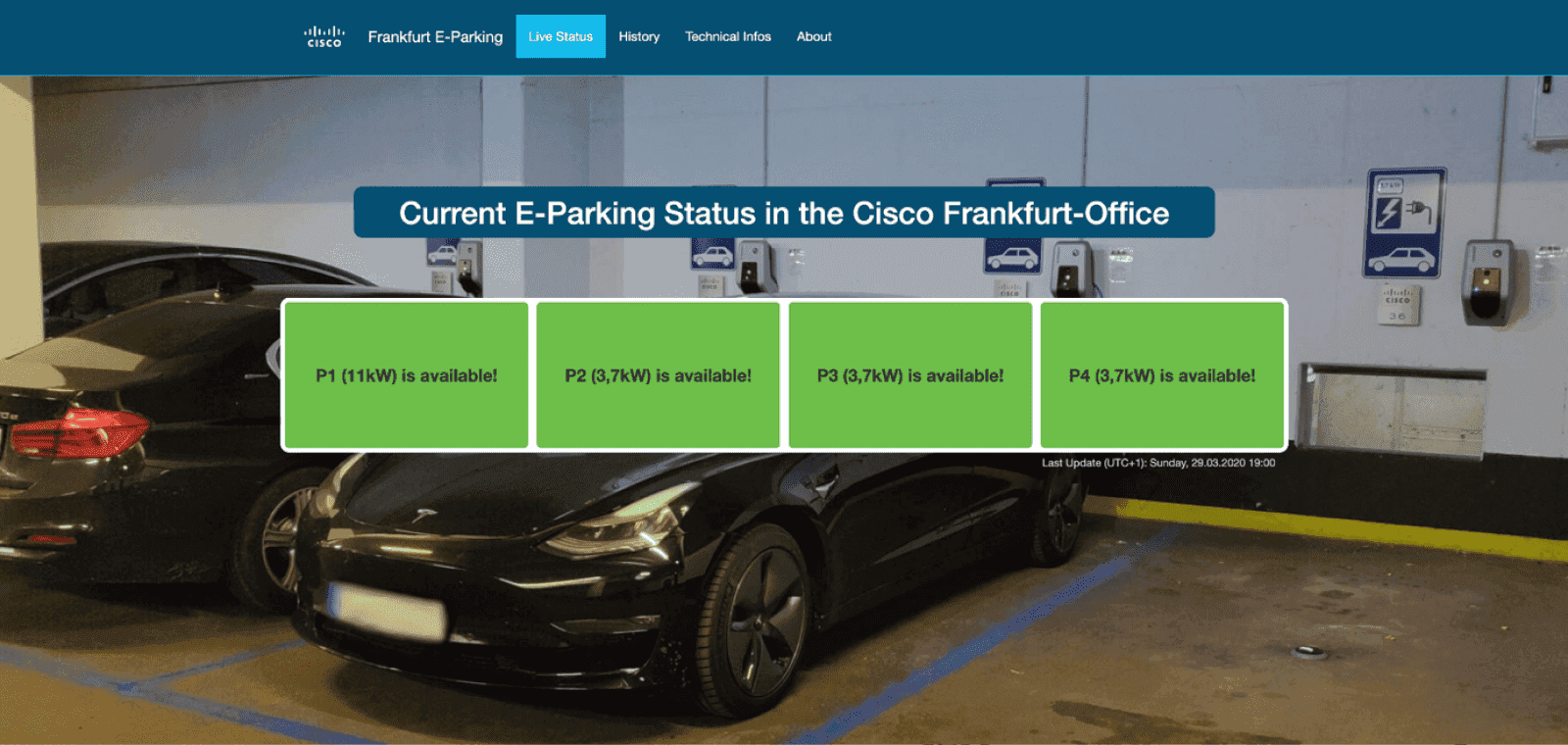
Image title: Cisco’s e-parking web portal as a part of the IoT solution
Data source: blogs.cisco.com — Smart Parking: A Cisco IoT Solution with LoRaWAN
Smart thermostat control for Jack in the Box restaurants
Jack in the Box, an American fast-food chain restaurant, had trouble maintaining the heating, cooling and freezer temperatures across its 29 restaurant locations. Due to old thermostats, the temperature changed without warning and required manual checks. To turn the corner on this temperature issue, Jack in the Box implemented intelligent building systems with thermostats that enable remote monitoring and control of the temperatures of the air conditioning systems as well as the freezers in all restaurant locations. Smart thermostats are equipped with sensors that send alerts whenever the temperature in a freezer significantly changes. As a result, each restaurant location saves around $500 on HVAC service due to IoT implementation.
Image title: Smart HVAC controller
Data source: ecobee.com — Jack in the Box
Smart access control for the Academy of Art University
With around 18,000 students and a large number of buildings and facilities, the Academy of Art University wanted to keep track of students’ movement across campuses and minimize the risks of thefts or intrusion. The Academy installed 200+ proximity readers on all exterior doors of its buildings. The system can be managed from a single command center on the main campus 24/7. The students receive unique cards to access the Academy’s buildings. The cards can also be used to pay at food service venues across the campuses and use the free shuttle the Academy provides for its students. Badges can also be programmed to provide short-term access to specific areas and can be disabled anytime.
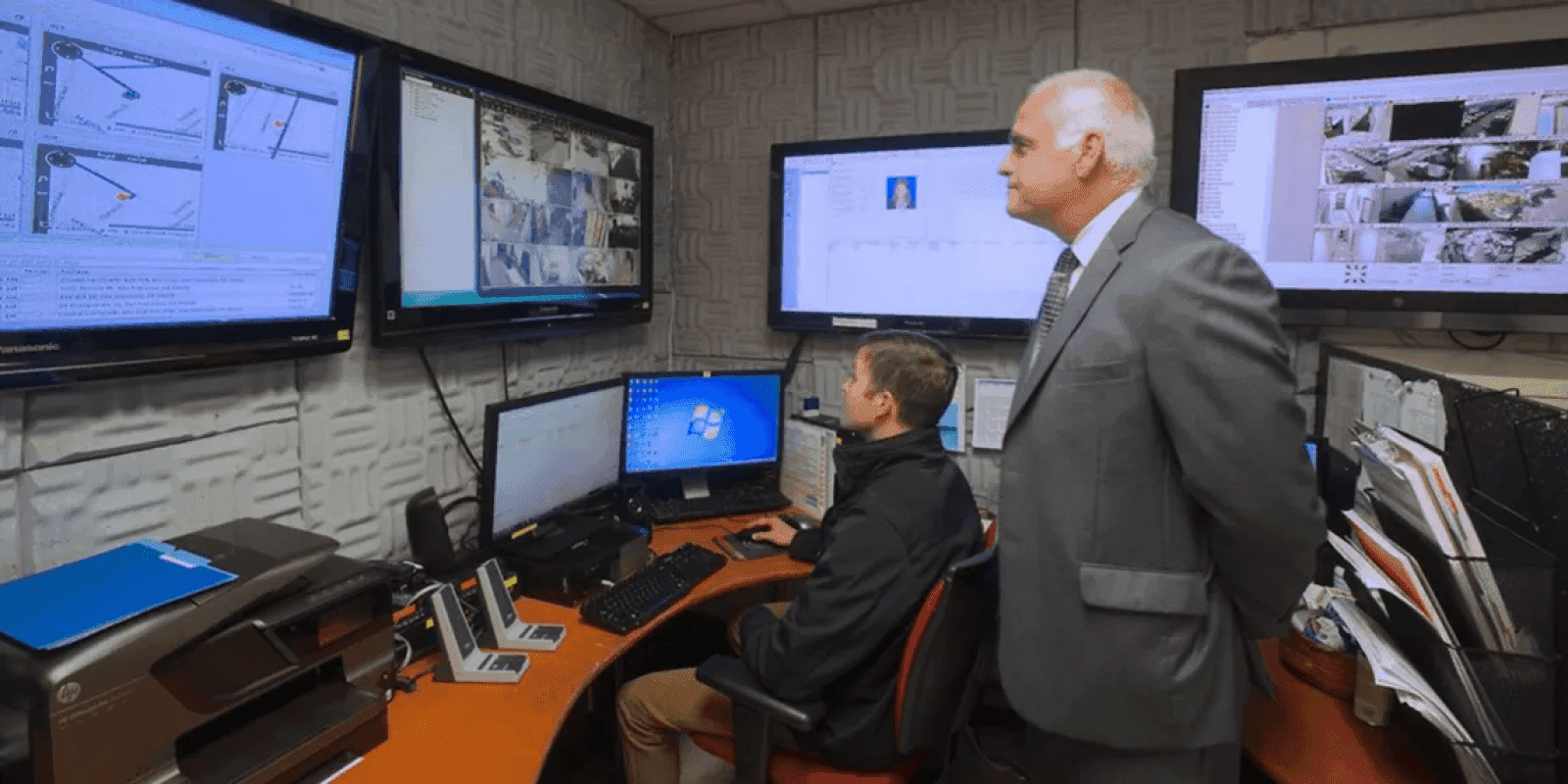

Image title: Smart access control for the Academy of Art University
Data source: buildings.honeywell.com — Academy Of Art College
Enterprise IoT trends
Here are our top 5 technology trends set to advance or optimize IoT systems employed across enterprises.
With the help of 5G, occupancy management can be more efficient due to better sensor connectivity in buildings. This will prove especially useful for large facilities with many assets to monitor and maintain.
Moreover, industrial IoT can significantly benefit from 5G adoption. Operating assets and manufacturing lines can be visually inspected with remote controllers. Then, taking advantage of low latency, an AI-powered system will analyze the received data about product or equipment defects faster.

Edge computing
While traditional IoT devices collect data and transmit it to the cloud storage for further analysis, edge computing allows for bringing the analytical component closer to the data source and network edge to gather and process information. IoT systems benefit from having the analytical center closer to the data source since it decreases communication latency between IoT devices and networks, speeds up response time, increases operational efficiency, and swift decision-making.
With edge devices incorporated into smart grids, enterprises across industries can better manage their energy consumption levels. At the same time, manufacturers can improve their predictive equipment maintenance, and healthcare organizations can better track unusual patient behaviors.
Scheme title: Reasons for edge computing in IoT adoption
Data source: iotbusinessnews.com — IoT Signals, 2021
Organizations that use IoT for these use cases and believe IoT is 7%+ more critical to organizational success.
Ranked top 5 most important
Digital twins
A digital twin replicates a physical object in the digital world. In IoT, digital twins are models of sensors, machines, or an entire infrastructure like a smart building or a manufacturing plant. With a digital twin, companies can simulate the behavior of physical objects under various conditions, test scenarios before implementing changes in the real world, and monitor physical assets’ performance and condition in real-time.
Scheme title: Benefits of using digital twins in IoT
Data source: iotbusinessnews.com — IoT Signals, 2021
Ranked top 3 benefits gained
*for a new product
Voice user interfaces and natural language processing
Top enterprise IoT platforms
Key features
- A ready-made UX and APIs for easy enterprise-wide IoT system creation
- A cloud platform for connecting, monitoring, and configuring IoT devices
- Digital representations of real devices, systems, and processes
- Enables edge computing on IoT devices
- Robust security for the protection of IoT devices
- Allows for the deployment of real-time applications on resource-constrained devices
Differentiators
- Seamless integration with other Microsoft products
- Suitable for .NET projects
- Scalable, flexible and easy-to-navigate development and deployment infrastructures
Limitations
- Fewer IoT offerings compared to AWS
- Limited device compatibility with specialized or industry-specific devices
Key features
- Building and managing IoT device software
- Capability for analysis of massive volumes of data from IoT devices
- MQTT protocol with low latency and high throughput for superior device-to-device communication
- Collecting, processing, and transmitting real-time data in the cloud
- Allows for creating digital twins of real-life systems, buildings, and operations
- Uninterrupted management of IoT security
- Early response to incidents
Differentiators
- More IoT offerings than Azure
- Strong development community providing valuable resources, documentation, and support
- Robust IoT infrastructures and excellent scaling capabilities on demand
- Support of a wide range of IoT devices due to Amazon’s partnerships with device manufacturers
Limitations
- A steep learning curve for non-AWS users
- Complex pricing system
Need help choosing an optimal IoT development tool?
Benefits of IoT in enterprises
Reduced operating costs
By implementing IoT solutions, businesses can set up predictive maintenance and save on considerable equipment repair costs. For example, utilizing the power of real-time data analysis, smart building systems allow companies to monitor and control HVAC systems and take action before disruptions occur, reducing repair expenses.
Optimized energy management
IoT sensors and devices can monitor energy consumption levels in the office. Relying on data from occupancy monitoring sensors, enterprises can set up an automatic system for thermostats and HVAC systems regulation, reducing energy consumption and lowering utility costs.
Higher workplace productivity
IoT technologies create a more productive work environment by automating such routine tasks as checking room availability and room booking. Smart meeting rooms with IoT-enabled devices like smart boards or interactive displays can also foster employee communication and collaboration. Moreover, with sensors continuously monitoring indoor air quality, temperature, humidity, and lighting, enterprise IoT can make the working environment more comfortable.
Improved workplace safety
IoT systems help ensure workplace security by providing real-time perimeter monitoring and allowing for early threat response. Integrated into smart office buildings, sensors, surveillance cameras, and IoT access control systems help monitor the employees' and equipment's safety and protect offices against intrusions and physical attacks.
Challenges in implementing IoT in enterprises
Despite the growing number of IoT use cases, about 35% of IoT projects fail during PoC or trial stages, according to a study by Microsoft. Here are the most common problems companies face when adopting IoT in their enterprises and how to overcome them.
Challenge
Solution
Security
Smart devices, IoT gateways, and data centers collect, process, and store sensitive data, which makes them an attractive target for hacker attacks. However, many IoT devices lack the computational capacity for built-in security mechanisms and receiving updates over the internet, which allows cybercriminals to gain access to enterprise infrastructure.
Smart devices, IoT gateways, and data centers collect, process, and store sensitive data, which makes them an attractive target for hacker attacks. However, many IoT devices lack the computational capacity for built-in security mechanisms and receiving updates over the internet, which allows cybercriminals to gain access to enterprise infrastructure.
- Ensure the physical security of your IoT devices by implementing port locks or camera covers.
- Install patches and updates regularly and run regular penetration testing to detect vulnerabilities in IoT device firmware and software.
- Secure IoT networks with solid data encryption and secure communication protocols. Make sure to adjust the device’s bandwidth and limit the network traffic to the amount necessary for its functioning.
- Collect only necessary data and protect sensitive data with robust authentication.
Finally, we recommend attracting experienced IoT software developers and cybersecurity experts to ensure your IoT system follows the NIST guide on IoT device cybersecurity.
Change management
Many companies treat IoT implementation solely as a tech project rather than a comprehensive digital transformation. As a result, IoT adoption projects tend to fail due to employee resistance and poor adoption.
Many companies treat IoT implementation solely as a tech project rather than a comprehensive digital transformation. As a result, IoT adoption projects tend to fail due to employee resistance and poor adoption.
When adopting IoT, you need to take into account the people and processes in your organization. Prepare a vision of how IoT will improve the organization’s workflows and ensure everyone is acquainted with future plans. During the IoT implementation, create bidirectional communication channels for employees to share their feedback. If the IoT adoption is a significant transformation, companies should turn to an IoT consulting company to guide them through establishing a new digital culture and practices.
Interoperability and compatibility
Interoperability and compatibility issues arise when different elements of the IoT ecosystem (devices, platforms, and protocols) utilize different architectures and data formats to communicate. Lack of interoperability prevents the adoption of more complex IoT technologies, machine learning, or digital twins and leads to vendor lock-in.
Interoperability and compatibility issues arise when different elements of the IoT ecosystem (devices, platforms, and protocols) utilize different architectures and data formats to communicate. Lack of interoperability prevents the adoption of more complex IoT technologies, machine learning, or digital twins and leads to vendor lock-in.
Although today many IoT platform vendors are working together to ensure superior interoperability and more centralized architectures of IoT devices, enterprises can also take several steps to ensure their IoT devices are interoperable and compatible.
- Before the implementation, carefully compare IoT devices and opt for those that are compatible with your existing infrastructure and platforms. Using APIs and standardized protocols such as MQTT, CoAP, or HTTP will streamline device communication.
- Adopt an IoT platform that will serve as a mediator and translator between different protocols during IoT device communication.
- Prior to IoT deployment, perform thorough testing to verify IoT components' interoperability and identify any potential issues early on.
Transforming enterprise management with the IoT
The Internet of Things is reshaping the ways enterprises handle their assets and operations. Despite apparent and inevitable adoption challenges, organizations are increasingly interested in IoT to digitalize and streamline enterprise workflows. IoT emergence and adoption helps companies reduce operational costs, improve employee productivity, optimize office energy consumption, and ensure the security of their staff and buildings.

Service
Internet of Things software development
Professional IoT development services to deliver IoT solutions that efficiently manage the network of connected devices and generate real-time insights.
Service
IoT consulting services
Itransition offers IoT consulting services to provide businesses expert guidance through their IoT projects and ensure the solution’s efficiency and high ROI.

Insights
IoT data analytics: components, use cases & adoption guidelines
Learn about the architecture, main benefits, use cases, and prominent real-life examples of IoT data analytics and explore a detailed implementation guide.

Insights
IoT implementation: a step-by-step guide, benefits, challenges & their solutions
Explore the step-by-step guide for IoT implementation, along with its industry use cases, benefits, and common challenges and efficient ways to overcome them.

Insights
Top IoT use cases & statistics for 2026
Explore 35 IoT use cases across various industries, top market statistics for 2026, and best practices for IoT adoption.

Insights
IoT architecture: key layers, components & use cases
Itransition shares a detailed structure of a typical IoT architecture and describes essential elements and factors to consider when choosing an IoT solution.

Insights
History of the Internet of Things: key milestones & future prospects
Learn about the history of the Internet of Things, including its key milestones with future opportunities, as well as IoT main benefits and roadblocks.

Insights
Industrial IoT: market trends & use case statistics
Discover recent market statistics on the industrial IoT market state and popular use cases, along with insights into its complementary technologies and benefits.